| Lesson Plans | Fact Sheet | Common Core Reading |
|---|---|---|
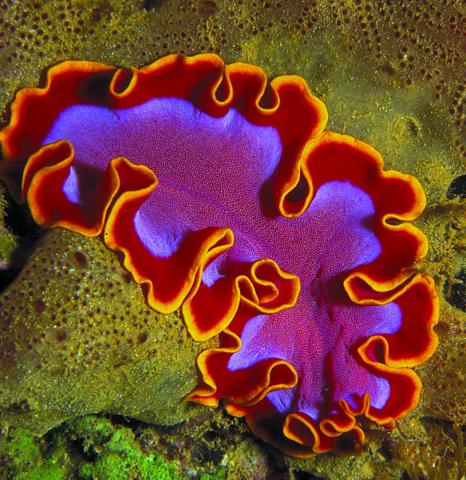
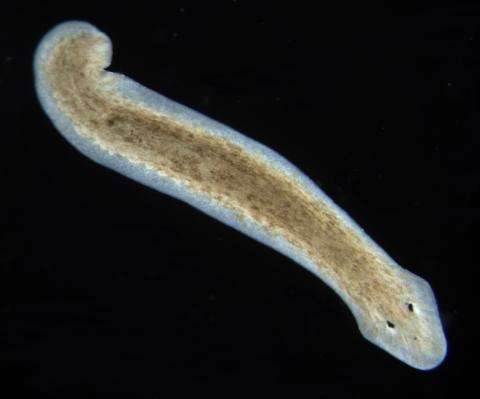
| Flatworms: The First Hunter Fact Sheet |
Videos
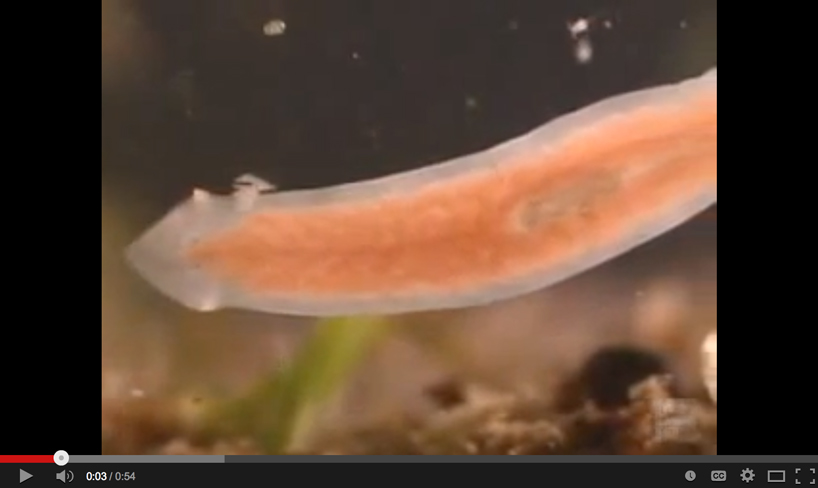

Planaria illustrates bilateral symmetry.
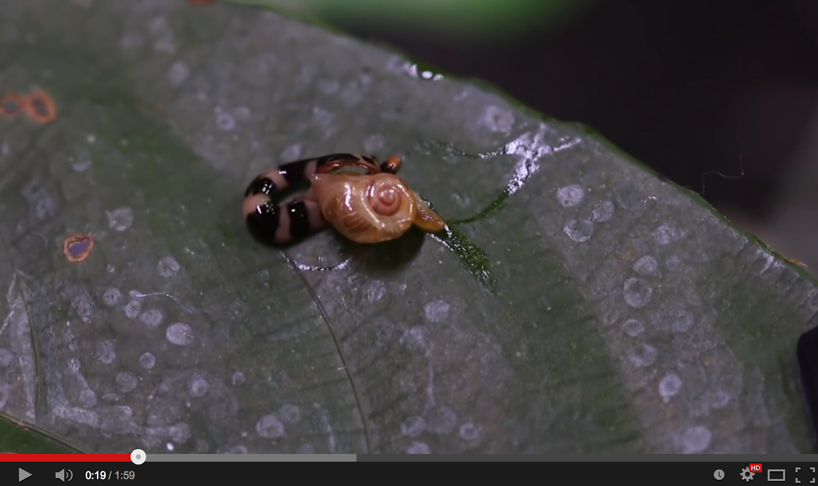

A predatory flatworm hunts a snail, on land

Flatworm swimming
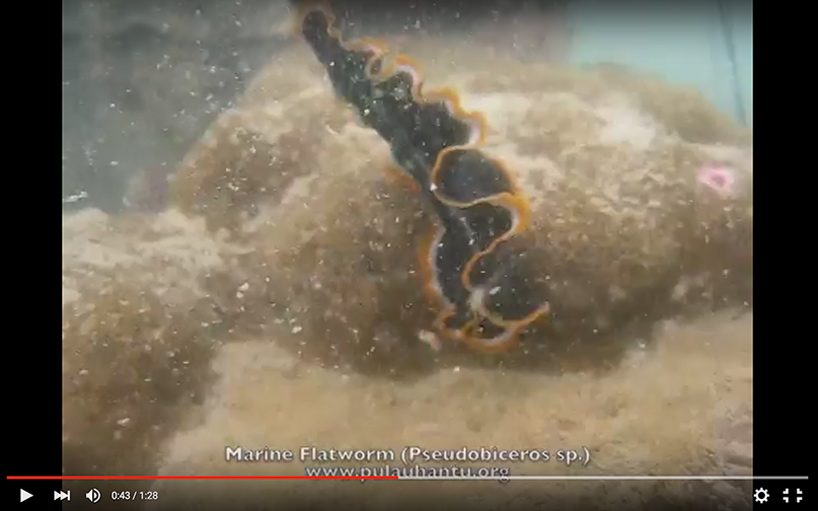

A flatworm lifting off from a coral reef and swimming
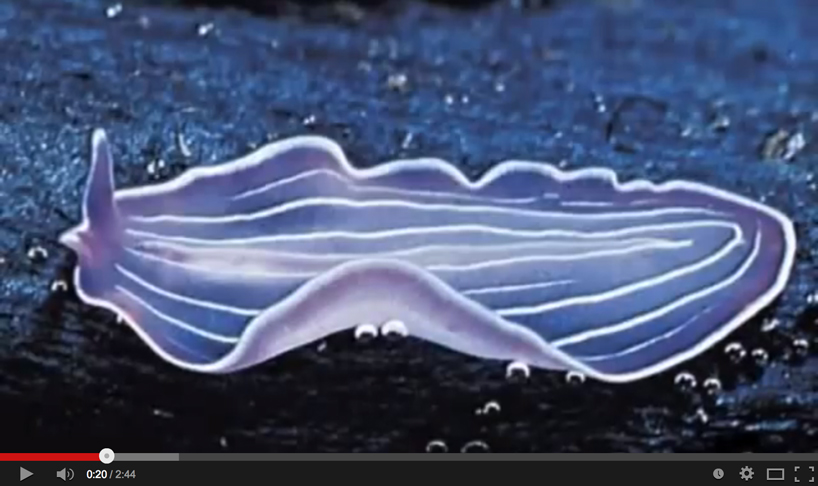

A song, with video about flatworms
Reading
GETTING A HEAD The First Hunter
Excerpt from the Shape of Life book.
GENERAL INFORMATION ABOUT FLATWORMS
- Read about flatworms.
- General information about flatworms
- Read about the advantages and disadvantages of being hermaphroditic
- A primer on marine flatworms for K-12 Students
- From the Museum Victoria (Victoria, Australia) more about marine flatworms
- Read about a cave-dwelling freshwater flatworm
- A large group of flatworms are parasites that can infect humans causing diseases, read the article.
FEATURED CREATURE
The Crazy World of Penis Fencing
The Badass New Guinea flatworm, Platydemus manokwari
ORIGINS
Researchers say tiny marine worms called acoels may be one of the closest living representatives of the first bilaterally symmetrical organisms. Using DNA analyses, the team concludes not only that the acoels don't belong with other flatworms, but that they alone represent a living relic of the transition between radially symmetrical animals such as jellyfish and more complex bilateral organisms such as vertebrates and arthropods. From a Flatworm, New Clues on Animal Origins.
Scientists found fossil tracks of the earliest bilateral animal from at least 585 million years ago. The tracks they found indicated a front and back as well as a top and bottom. Fossil of Early Bilateral Animal.
Researchers at the University of California, Davis, discovered a bi-lateral worm-like fossil from before the Cambrian Explosion. This suggests that a bilateral body plan may have evolved earlier than previously thought, read more.
FLATWORMS AMAZING ABILITIES
Some flatworms use the mitochondria in some cells (which we all have) in their heads to form lenses to focus light onto their light sensitive cells. Read the article on Creature Cast.
Planarians can regenerate body parts including growing a new head and brain. When scientists studied the process identified the gene that makes this possible and that the planarians have stem cells to make these new body parts. Read more.
Scientists are investigating how planarians maintain the stem cells that let them regenerate. Learn more.
ROLE IN ECOSYSTEM
Invasive flatworms can cause major disruptions to ecosystems: read about an invasive flatworm on the Shape of Life website.
Researchers at the University of New Hampshire found that flatworms in estuaries can indicate the health of the ecosystem.
Flatworms play a role in many food chains. Read about some of them.
Parasitic flatworms can disrupt ecosystems. Learn more.
HUMAN USE
Some flatworms, planaria, can be used as models for toxicology (2015). Read an article from UC San Diego: "Flatworms Could Replace Mammals for Some Toxicology Tests".
PHOTO RESOURCES
Platyhelminthes from the Florida Museum of Natural History.
The Marine Flatworm Galleries.