| Lesson Plans |
Fact Sheet |
Common Core Reading |
|---|---|---|
| Phylum Arthropoda Fact Sheet |
Videos
All about marine arthropods, with animation by a high school class.
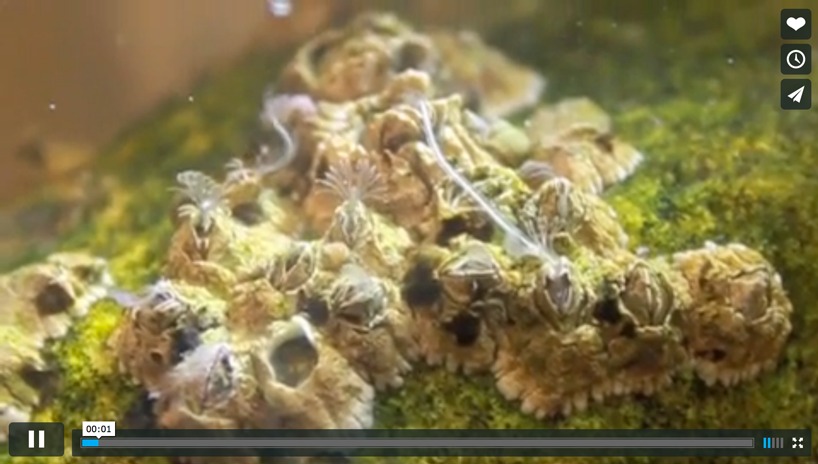

X-rated high school only: If, like barnacles, you’re stuck on rocks, it helps to be a hermaphrodite—having both male and female organs. During mating season, barnacles are functionally one sex or another. The functional males have very long penises, which they insert into mates, releasing sperm.
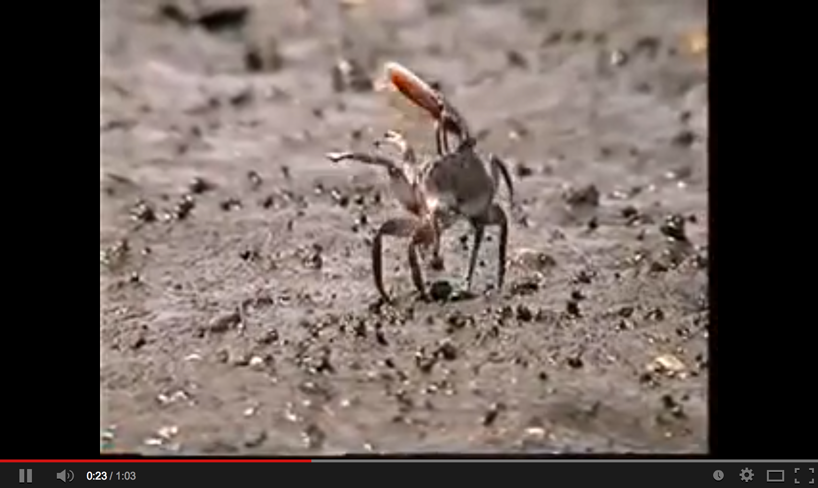

Fiddler crab males do a waving dance to attract females
ROLE IN ECOSYSTEM

In the Antarctic, krill are the dominant zooplankton, essential food for penguins, seals and whales. They swim by the billions in Antarctic seas feeding predators there. And many factors threaten this key species as shown in this video.
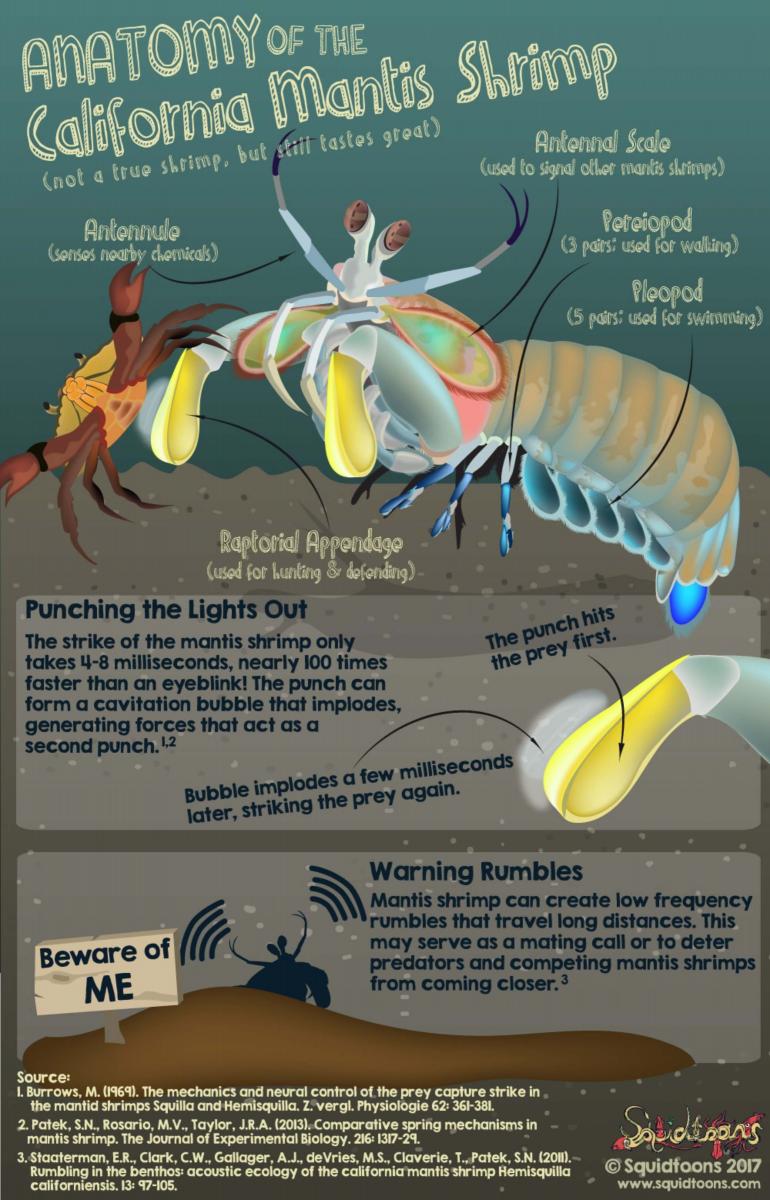
ANATOMY OF A MANTIS SHRIMP
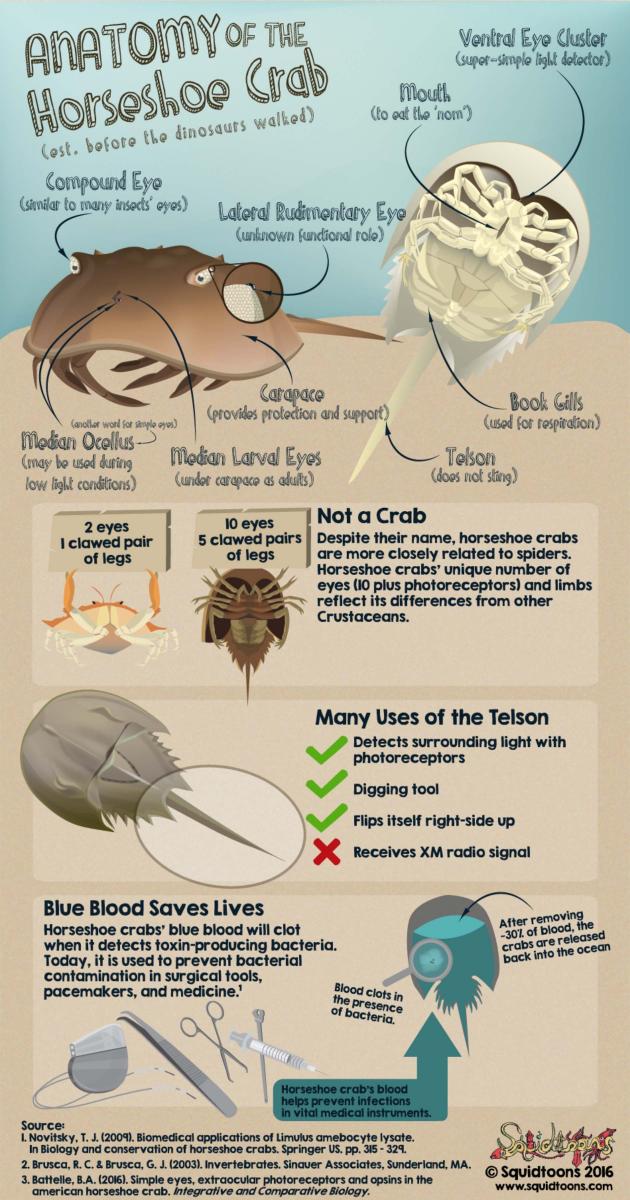
ANATOMY OF A HORSESHOE CRAB
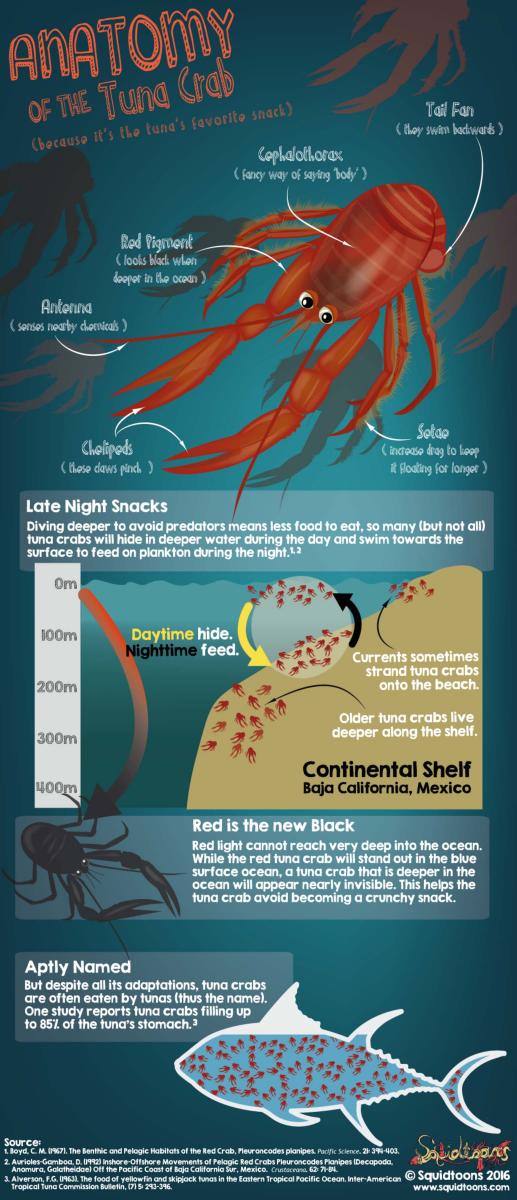
ANATOMY OF A TUNA CRAB
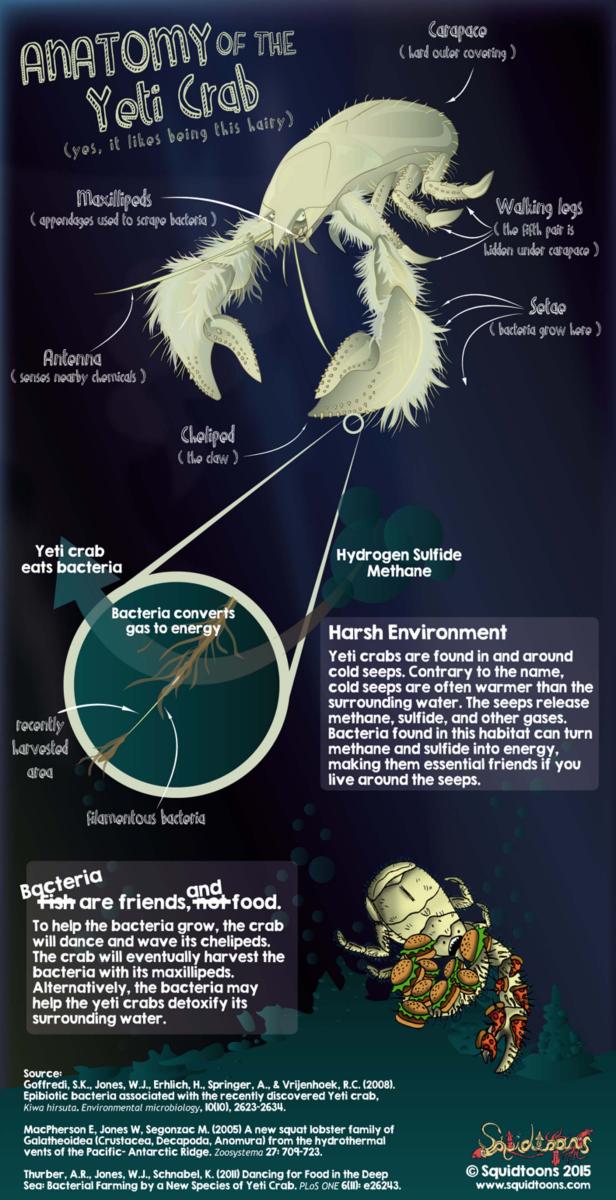
ANATOMY OF A YETI CRAB
Reading
THE MARINE ARTHROPODS A Successful Design
Excerpt from the Shape of Life book.
GENERAL INFO ABOUT MARINE ARTHROPODS
From Understanding Evolution - your one stop source for information about evolution: Read about the evolutionary history of arthropods.
Arthropods have segmented bodies, a key to their success. Read an article from Science Daily: "Segmentation is the secret behind the extraordinary diversification of animals".
Christmas Island crabs are land crabs that begin their lives in the sea. The crabs spawn at the edge of the sea where the tiny crab larvae begin their lives. After several larval stages, the tiny crabs go back to the land. From the Australian Government Department of the Environment, read about Red Crab Migration.
Christmas Island National Park, Australia article: "Red crabs Gecarcoidea natalis".
Christmas Island National Park, Australia article: "Viewing the annual red crab migration".
From Ocean Conservation Research, learn about snapping shrimp. You can read about them and listen to the sound here.
General facts about tropical lobsters called spiny lobsters from the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission.
All about the American lobster, from NOAA general information about lobsters.
Lobsters are delicacies on menus as are crab. Read about the life history of the Dungeness crab, a west coast seasonal favorite.
Marine arthropods, like crabs, go through various stages and forms before they reach their adult body form. Read about the life cycle of a blue crab.
Photo of Dungeness crab larva.
November 2015. California fishery officials closed down both the commercial and recreational Dungeness crab fishery due to a toxic algae bloom. Read about and listen here.
Chitin is a major component of the exoskeleton of marine arthropods. Read about chitin and how prevalent it is in the animal world.
Read about how chitin is being used as surgical thread.
Blue crabs are very tasty eating. Here’s some information about eating them in their hard-shell stage.
Soft-shell crabs are also a popular dish. These are crabs that have molted their hard exoskeletons and haven’t yet grown a new one. This explains how to find and catch soft shell crabs.
This intertidal crab has a way of hiding in plain sight: it decorates itself to look like a rock covered in other animals or seaweed. The crab decorates by attaching material to its shell. Read about the decorator crab on the Monterey Bay Aquarium website.
FEATURED CREATURE
Thank Goodness We've Got Crabs!
ROLE IN ECOSYSTEM
Copepods are tiny marine arthropods that are very diverse and are the most numerous multi-celled animals in the aquatic community. As zooplankton, they play a major role in the ocean’s food web.
Krill are another tiny arthropod that make up a large portion of the zooplankton in many regions of the ocean. Swarms of krill feed the largest creatures in the ocean, blue whales, as well other whales, sea birds, squid and fishes. They play a major role in the ocean’s food web.
Sea spiders, or pycogonids, are not spiders at all. They’re a group of marine arthropods that live from the intertidal to the deep sea. Sea spiders feed by sucking up soft-bodied invertebrates whole and by sucking the juices using a long proboscis.
Read about the impact that copepods have on transport of carbon dioxide in the ocean (2015).
HUMAN USE
Collecting horseshoe crabs' blood for medical uses. Biotech companies harvest horseshoe crab blood for a compound that can detect practically any amount of bacterial contamination.
Krill in the supermarket aisles.
PALEONTOLOGY
Scientists have found evidence of a complex brain in a fossil arthropod that’s estimated to be 520 million years old. The extinct crustacean’s brain supports some scientists’ hypothesis that once a basic brain evolved, it changed little.
Trilobites once were the dominant species in the marine environment. They ranged in size from a quarter inch to dinner plate size and had complex behaviors. And as predators evolved, so did the complexity of trilobite defenses and their eyes. The number of trilobites decreased in the end of the Paleozoic and vanished in the end-Permian extinction.
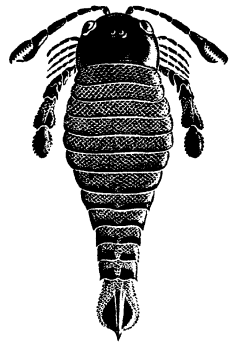
In 2015 scientists have discovered a fossil of giant sea scorpion, read about it in Yale News.
CITIZEN SCIENCE
On the west coast of the U.S., students participate in a beach monitoring program called LiMPETS (Long-term Monitoring Program and Experiential Training for Students). Students either participate in monitoring sandy beaches or the rocky intertidal. Not only are students contributing to knowledge about changes to these environments, they’re also learning the scientific process. Learn about the program.